This page provides for download a computer program to calculate and print out sight reduction tables similar to the classic ‘Air Tables’. Compiled versions for Windows PC and Apple Mac computers are provided, we also provide ‘C’ source code that can be compiled for other operating systems.
When running the program one can select the Latitude and Declination ranges to be printed which means that in practice there is no need to make a thick book; a suggested use is to print off the few pages covering the ranges of Latitude and Declination, plus some safety margin, relevant to the planned voyage.
- Disclaimer
- Tables
- Sign convention
- Files for Download
- Support
- Generating tables
- Printing them out
- Using the tables
Disclaimer
To the best of our knowledge the downloads provided here generate accurate tables, however anyone using the generated tables does so at their own risk, we make no warranty about the accuracy of the tables generated by these downloads.
The downloads provided on this page are copyright of James Collier.
Tables
The tables display calculated Altitude and Azimuth for LHA versus Declination, one page for each degree of Latitude. A snippet of a page is reproduced here:
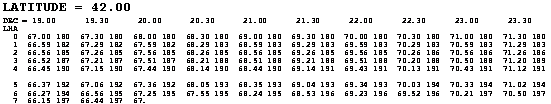
The Declination is printed across the top, in half-degree (30 minute) intervals, and the LHA down the vertical axis, starting at zero and going up to 109 degrees (by which time the sun would be below the horizon!). Each entry contains a two number pair: the calculated altitude and the calculated azimuth. Look at the values in the table above for LHA = 3° and Declination = 20° 30’; the Calculated Altitude is 68° 21’ and the Calculated Azimuth is 188°.
The format of the tables is always dd.mm, that is to say degrees, a decimal point, then minutes.
Sign convention
The following convention is used – it may be idiosyncratic:
- Latitude is positive if north, negative if south
- Declination is positive if north and negative if south
- LHA is positive when the sun is west of one’s estimated position Azimuth is in degrees true.
- Altitude can be used directly
- Azimuth = 360 – tabulated Azimuth.
Files for Download
This site only contains a small example file of a pre-prepared table, so you have to compute and print your own. The files available for down-load are:
- The program in Windows PC or Apple MAC format.
- The program is a single file, ‘gen_table’ which is the actual program that creates the tables (as rtf documents, see above). Before using this program for navigation you must read our disclaimer.
- An example of the output of the program.
- It is a text file which is readable by Microsoft ‘Word’ or virtually any other word processing package. The format is known as ‘Rich Text Format’ which determines the font, its size and spacing, so one degree of Latitude should fit exactly on one page.
- The source code of the program which generates the tables, main.c.
- You should not really need this file, but it is included for interest’s sake or for those who do not use either a PC running Microsoft Windows or an Apple Mac running OS X, and therefore need to compile the program. (Don’t worry if this means nothing to you – you don’t need the file in that case! It is customary at this point to welcome feedback on the program; the author is already aware that their code contains many infelicities, but if you spot that the program actually gives incorrect answers please do let us know.)
Support
Please note that we are unable to provide any support for this software and cannot answer support requests relating to these downloads, but they are provided free of charge so if they work on your system that's fine.
Generating tables
Having downloaded the program file ‘gen_table’, (it may be shown as ‘gen_table.exe’ on some computers), you are ready to run it. To do so open a command window:
- PCs: Click on the Windows icon in the south-west corner of the screen, then click on ‘Run…’ and type ‘cmd’ in the dialogue box displayed.
- MACs: In ‘Finder’ look in ‘Applications’ then ‘Utilities’ and then click on ‘Terminal’.
In both cases you must change directory (command is ‘cd’) to wherever you have put the downloaded file ‘gen_table’. At this point you may run the program by typing, for eacmple:
- PCs:
- gen_table 0 2 15 20
- MACs:
- ./gen_table 0 2 15 20
What this does is run the program, and you should see pages of text rushing past on the screen. The four numbers are the variables or ‘arguments’ that determine the range of latitude and declination to be covered, they are entered in the following order:
- Start Lattitude (=0 in the example above)
- Finish Lattitude (=2 in the example above)
- Start Declination (=15 in the example above)
- Finish Declination (=20 in the example above).
Only 13 columns fit across an A4 sheet of paper, so I suggest that you always choose Start Declination and Finish Declination which are 6 degrees apart (the Declination is printed every half degree, so 6 degrees means 13 columns – think about fences and gateposts).
Important: A peculiarity of the program is that the input values are in degrees, not degrees.minutes, so to start at a Declination of 17° 30’ one types 17.5.
This directs the output to a file called "tmp.rtf" . There’s nothing magic about this name, by all means change it to any name you like, such as “Some output from this rotten programme.rtf”. But keep the" .rtf" on the end.
Printing them out
Open the rtf file just created in your favourite word processor and it should look neat, Latitude value printed at the top, 13 columns of Declination spaced half a degree apart and a row for every degree of LHA from 0 to 109, all fitting on a single page for every value of latitude printed.
Assuming it does look like this, just print the file just as you would any normal document. The paper size has to be A4.
Using the tables
It is assumed that you are already familiar with using a sextant and the concepts by which one uses sun sights to establish a position line – terms such as Declination and LHA have already been used. However here is the way I think about the problem and the way I use the tables:
- Look up Declination and GHA
- At any given moment the sun is due overhead at one spot, and with a nautical almanac one can look up the Latitude (which is called Declination) and Longitude (which is called ‘Greenwich Hour Angle’) of this spot. These are usually tabulated every 2 hours and one has to interpolate to a couple of seconds accuracy. One can interpolate the Declination by eye since it changes slowly, but to interpolate the GHA one uses the fact that the earth rotates 15 per hour (thus 360 in 24 hours). Use either a calculator or the GHA correction table in Reeds to work it out to the nearest second.
- Estimate your own position (EP)
- For the purposes of a sun sight choose the position close to where you think you are but at a whole degree of Latitude, and at a Longitude such that the LHA is a whole number of degrees: LHA = GHA – Longitude.
- Look up the Altitude and Azimuth Using the tables!
- Now it’s obvious why the EP has been chosen in the arcane way described above, since Longitude and LHA are whole numbers of degrees one has to interpolate only for Declination, which I find I can do in my head. The altitude taken from the table is known as Calculated Altitude, CA.
- Measure the True Altitude
- Using your sextant measure the actual altitude, applying all the normal corrections for parallax, height of eye and semi-diameter. This is the True Altitude.
- Difference the TA and the CA
- This difference, in minutes, is the distance in nautical miles between the EP and the position line on which you actually are according to the sun sight; when True Altitude is greater than Calculated Altitude your position must be closer to the sun than the EP – pretty obvious really, the closer one is to the sun the higher it is in the sky.
- Plot the position line
- Put a point on the chart or plotting sheet at the distance just calculated in step 5 from the EP along a bearing equal to the Azimuth. Then draw a line through this point at right angles (to the Azimuth). This line is the position line. You are on it somewhere, but not necessarily at the point closest to the EP.